Infertility is a complex issue that affects millions of couples worldwide, and it’s a particularly challenging journey for women. Female infertility can be caused by a variety of factors, both physiological and psychological. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring treatment options are crucial steps in navigating this journey toward parenthood.
Causes of Female Infertility
Ovulation Disorders
- Ovulation disorders are among the most common causes of female infertility. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), hypothalamic dysfunction, and premature ovarian failure can disrupt the ovulation process, making it difficult for women to conceive.
Fallopian Tube Damage or Blockage
- Damage or blockage of the fallopian tubes can prevent the egg from meeting the sperm, thus hindering fertilization. Causes of fallopian tube damage include pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), endometriosis, and previous pelvic surgery.
Uterine or Cervical Issues
- Abnormalities in the uterus or cervix can affect fertility by interfering with implantation or the passage of sperm. Conditions such as uterine fibroids, polyps, or cervical stenosis may contribute to female infertility.
Endocrine Disorders
- Hormonal imbalances, such as thyroid disorders or hyperprolactinemia, can disrupt the menstrual cycle and impair fertility. Proper hormonal regulation is essential for ovulation and the maintenance of a healthy reproductive system.
Age
- Age plays a significant role in female fertility, with a decline in fertility occurring as women age, particularly after the age of 35. Advanced maternal age is associated with decreased ovarian reserve and an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities in eggs.
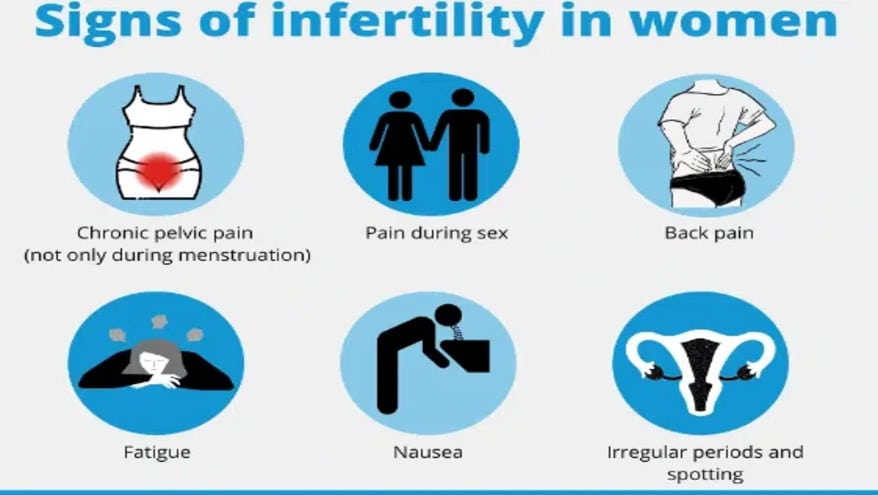
Symptoms of Female Infertility
Irregular Menstrual Cycles
- Irregular or absent menstrual cycles may indicate underlying ovulatory disorders, such as PCOS or hypothalamic dysfunction.
Painful Periods
- Severe menstrual pain, especially during ovulation or menstruation, could be a symptom of conditions like endometriosis, which may impact fertility.
Abnormal Vaginal Discharge
- Unusual vaginal discharge or pelvic pain may be signs of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can lead to fallopian tube damage and infertility if left untreated.
Hormonal Imbalances
- Symptoms of hormonal imbalances, such as excessive hair growth, acne, or changes in libido, may indicate underlying endocrine disorders affecting fertility.
Previous Miscarriages
- Recurrent miscarriages or difficulties carrying a pregnancy to term may signal underlying issues with fertility or reproductive health.

Treatment Options for Female Infertility
Medication
- Fertility medications, such as clomiphene citrate or letrozole, can stimulate ovulation in women with ovulatory disorders like PCOS.
- Hormone therapy may be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles or correct hormonal imbalances affecting fertility.
Surgery
- Surgical procedures, such as laparoscopy or hysteroscopy, may be performed to correct structural abnormalities in the uterus, remove fibroids or polyps, or repair damaged fallopian tubes.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
- In vitro fertilization (IVF) involves fertilizing eggs with sperm in a laboratory setting and then transferring the resulting embryos into the uterus.
- Other ART procedures, such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), may be recommended depending on the specific fertility issues.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, can support overall reproductive health.
Emotional Support
- Coping with infertility can be emotionally challenging for couples. Seeking support from counselors, support groups, or online forums can provide emotional support and guidance throughout the fertility journey.
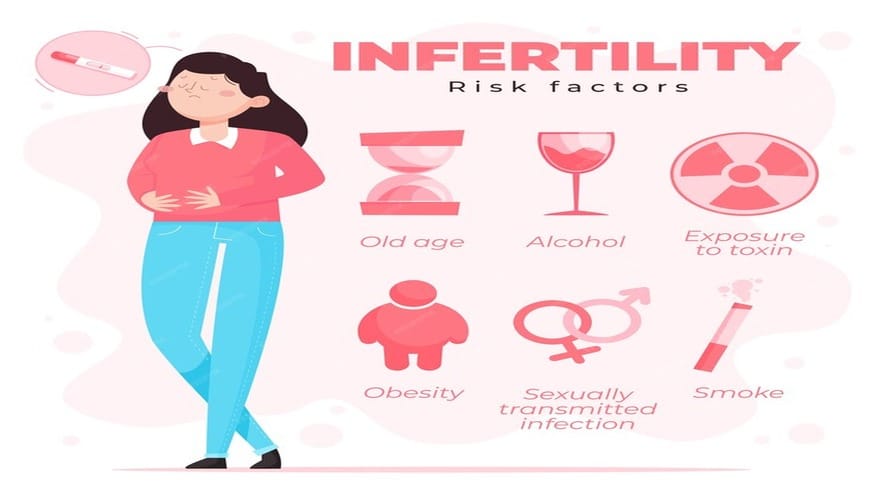
What are Risk Factors for Infertility?
Age:
- Women: Fertility declines with age, particularly after the age of 35, due to a decrease in the number and quality of eggs.
- Men: Advanced paternal age is associated with a decline in sperm quality and an increased risk of genetic abnormalities in offspring.
Lifestyle Factors:
- Smoking: Both men and women who smoke have lower fertility rates due to the harmful effects of toxins on reproductive organs and DNA.
- Alcohol and Drug Use: Excessive alcohol consumption and drug use can impair fertility in both men and women.
- Poor Diet and Obesity: Obesity and inadequate nutrition can affect hormone levels and reproductive function in both sexes.
Medical Conditions:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS often have irregular periods and may struggle with ovulation, leading to infertility.
- Endometriosis: This condition can cause scarring and adhesions within the reproductive organs, hindering conception.
- Fibroids: Uterine fibroids can interfere with implantation or block fallopian tubes, leading to infertility.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Untreated STIs such as chlamydia and gonorrhea can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), leading to scarring and damage to the reproductive organs.
- Thyroid Disorders: Thyroid imbalances can disrupt menstrual cycles and interfere with ovulation.
- Diabetes: Poorly managed diabetes can affect fertility in both men and women.
- Cancer and its Treatments: Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can damage reproductive organs and impair fertility.
Environmental Factors:
- Exposure to Chemicals: Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, such as pesticides, lead, and industrial pollutants, can affect fertility in both men and women.
- Heat: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures, such as in saunas or hot tubs, can temporarily reduce sperm production in men.
- Radiation: Exposure to radiation, whether from medical treatments or environmental sources, can damage reproductive cells and impair fertility.
Genetic Factors:
- Inherited Conditions: Genetic disorders such as cystic fibrosis or chromosomal abnormalities can affect fertility in both men and women.
- Family History: A family history of infertility may indicate a genetic predisposition to reproductive problems.
Psychological Factors:
- Stress: Chronic stress can affect hormone levels and menstrual cycles in women and reduce sperm quality in men.
- Mental Health Disorders: Conditions such as depression and anxiety can affect libido and sexual function, potentially impacting fertility.
Reproductive System Abnormalities:
- Blocked Fallopian Tubes: Obstructions in the fallopian tubes can prevent the egg from meeting the sperm, leading to infertility.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection can impede conception in men.
- Ejaculatory Disorders: Conditions such as retrograde ejaculation can prevent sperm from reaching the egg during intercourse.
- Structural Abnormalities: Congenital or acquired abnormalities of the reproductive organs can hinder conception.
These risk factors for infertility can vary in their significance from person to person and may interact with one another to influence fertility outcomes. Understanding and addressing these factors can be crucial for individuals or couples seeking to conceive.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the common causes of female infertility?
A: Common causes include ovulation disorders like PCOS, fallopian tube damage or blockage, uterine abnormalities, endocrine disorders, and advanced maternal age. These factors can disrupt the reproductive process, making it difficult for women to conceive naturally.
Q: How can irregular menstrual cycles affect fertility?
A: Irregular menstrual cycles may indicate underlying ovulatory disorders, which can hinder the release of eggs necessary for fertilization. Without regular ovulation, conception becomes challenging for women trying to get pregnant.
Q: What role does age play in female fertility?
A: Age significantly impacts female fertility, with a decline in fertility occurring as women age, particularly after 35. Advanced maternal age is associated with decreased ovarian reserve and an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities in eggs, making conception more difficult.
Q: Can lifestyle factors affect female fertility?
A: Yes, lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, stress, and substance use can impact female fertility. Maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress levels, avoiding tobacco, and limiting alcohol intake can support reproductive health and improve the chances of conception.
Q: What are some treatment options for female infertility?
A: Treatment options include fertility medications to stimulate ovulation, surgical procedures to correct structural abnormalities, assisted reproductive technologies like IVF or IUI, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause of infertility and the individual’s medical history.
Conclusion
Female infertility is a complex and often emotionally taxing condition that requires comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment. By understanding the underlying causes, recognizing symptoms, and exploring available treatment options, women can empower themselves to navigate the journey toward parenthood with resilience and hope. With advancements in medical technology and ongoing support, many couples struggling with infertility can ultimately achieve their dream of building a family.
Take the first step towards addressing your fertility concerns. Schedule an appointment with our experienced fertility specialists today. Let us guide you on your journey towards parenthood. Your dreams of starting a family are within reach. Contact us now to begin your personalized fertility assessment.
Schedule your appointment today at +1-212-794-8800 or email us at info@patientsmedical.com.
Our medical center is in New York City.
Patients Medical PC
1148 Fifth Avenue, Suite 1B
New York, NY 10128


