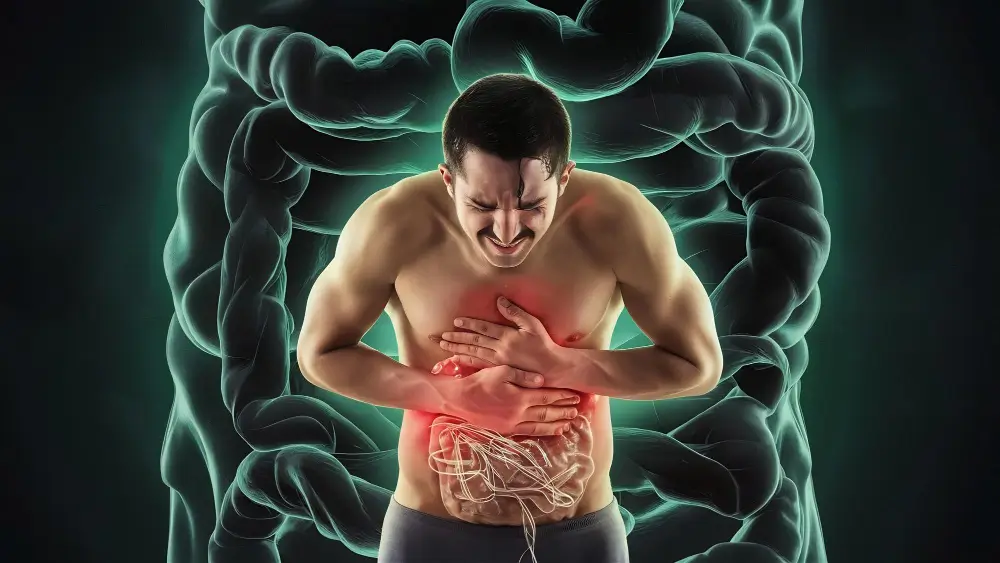
Your gut plays a central role in immune function — and when it becomes inflamed or “leaky,” it can trigger widespread symptoms including IBS, food sensitivities, chronic inflammation, fatigue, brain fog, skin issues, and even autoimmune conditions. This page explains how a damaged gut lining disrupts the immune system, why IBS is often a sign of deeper imbalance, and how functional medicine identifies and repairs root causes to restore long-term gut and immune health.
FAST FACTS
- Immune System Link: ~70% of the immune system lives in the gut
- Key Issues: Leaky gut (intestinal permeability), microbiome imbalance, chronic inflammation, IBS, food sensitivities
- Autoimmune Connection: Leaky gut is a major trigger for Hashimoto’s, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, IBD, celiac & other autoimmune disorders
- Common Symptoms: Bloating, irregular stools, abdominal pain, fatigue, joint pain, brain fog, skin flare-ups, nutrient deficiencies
- Functional Approach: Test → Identify triggers → Heal the gut lining → Rebalance microbiome → Calm immune response
HOW LEAKY GUT TRIGGERS IMMUNE PROBLEMS
- Inflammation: Food particles + toxins seep into bloodstream → chronic immune activation
- Autoimmune Activation: Overactive immune response begins attacking the body’s own tissues
- Microbiome Imbalance: Bad bacteria fuels inflammation and IBS symptoms
- Poor Nutrient Absorption: Low vitamin D, iron & B vitamins → fatigue + immune dysfunction
- Gut–Brain Axis: Leaky gut → leaky brain → mood swings, anxiety, cognitive issues
WHAT IMPROVES WHEN THE GUT HEALS
- Reduced bloating, gas & IBS symptoms
- Better immune balance — fewer flare-ups
- Clearer skin (eczema, psoriasis, acne)
- More energy & reduced inflammation
- Calmer mood, better sleep, clearer thinking
- Better thyroid & autoimmune stability
TOP QUESTIONS ANSWERED
- Can leaky gut cause IBS, autoimmune symptoms or chronic inflammation?
- How does gut permeability disrupt the immune system?
- What tests diagnose leaky gut & microbiome imbalance?
- Can healing the gut improve autoimmune symptoms?
- Which foods, nutrients & supplements repair the gut lining?
Recommended Next Steps
- Order a Comprehensive Gut & Immune Panel (stool test, zonulin, inflammation markers)
- Identify triggers — food sensitivities, infections, stress, toxins, gluten
- Begin a Gut Repair Protocol (remove → reinoculate → repair → rebalance)
- Support immune health with anti-inflammatory nutrition & lifestyle
- Follow a personalized functional medicine plan to manage IBS & autoimmunity long-term
Leaky Gut, IBS & Autoimmunity – The Gut-Immune Connection
For years, gut symptoms like bloating, pain, constipation, diarrhea, or food sensitivities were treated as “just digestive problems.” Today, science confirms that the gut plays a far bigger role — especially in immune function and chronic inflammation.
A damaged gut lining (often referred to as leaky gut) can trigger IBS symptoms, autoimmune flare-ups, chronic inflammation, fatigue, skin issues, and hormonal imbalance.
Up to 70% of your immune system lives in your gut. When the gut is inflamed or permeable, the immune system becomes confused, overactive, and reactive — laying the groundwork for autoimmunity.
This article explains how leaky gut develops, how it connects to IBS and autoimmune diseases, and what you can do to repair the gut-immune connection naturally.
What Is Leaky Gut?
The gut lining is supposed to be a tight barrier that absorbs nutrients while blocking toxins, pathogens, and undigested food particles.
When the lining becomes inflamed or damaged, the tight junctions loosen — this is known as increased intestinal permeability or “leaky gut.”
As a result, unwanted particles leak into the bloodstream, causing the immune system to overreact.
Common causes of leaky gut include:
- Chronic stress
- Poor diet (sugar, gluten, processed foods)
- IBS or chronic digestive inflammation
- Food intolerances
- Gut infections (SIBO, Candida, H. pylori)
- Toxins or heavy metals
- Long-term use of antibiotics, PPIs, NSAIDs
- Chronic inflammatory conditions
IBS and Leaky Gut — A Two-Way Relationship
IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) involves chronic digestive symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, or both.
Research shows that many IBS patients have:
- Low-grade gut inflammation
- Altered microbiome
- Increased intestinal permeability
- Heightened immune activation
This means IBS can cause leaky gut, and leaky gut can worsen IBS, creating a cycle of inflammation.
How Leaky Gut Triggers Autoimmunity
Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues.
Examples include:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriasis
- Lupus
- Celiac disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Type 1 diabetes
A damaged gut can leak particles like toxins and food antigens into the bloodstream.
The immune system responds by launching an inflammatory attack.
Over time, this can lead the immune system to misfire and attack your own organs or tissues.
Three main ways leaky gut leads to autoimmunity:
- Molecular mimicry – Foreign particles resemble your own cells, confusing the immune system.
- Chronic inflammation – Persistent gut damage keeps the immune system constantly “on.”
- Immune dysregulation – A damaged gut microbiome weakens immune tolerance.
This is why gut health remains one of the most critical foundations for managing or preventing autoimmune diseases.
Symptoms of Leaky Gut & Gut-Immune Dysfunction
You may experience digestive issues and systemic symptoms, including:
Digestive Symptoms
- Bloating
- Gas
- IBS (diarrhea, constipation, cramping)
- Reflux
- Food sensitivities
Whole-Body Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Brain fog
- Joint pain
- Rashes or eczema
- Weight changes
- Anxiety/depression
- Autoimmune flare-ups
When gut health is compromised, the entire body feels it.
Testing for Leaky Gut, IBS & Autoimmune Triggers
Functional medicine testing helps uncover what’s driving inflammation.
Common tests include:
- Comprehensive stool analysis (checks bacteria, yeast, parasites, inflammation markers)
- Intestinal permeability tests
- SIBO breath test
- Food sensitivity testing
- Autoimmune antibody panels
- Inflammation markers: CRP, ESR, cytokines
- Thyroid antibodies (Hashimoto’s often starts in the gut)
Proper testing guides personalized treatment.
How We Treat Leaky Gut at Patients Medical
We use an integrative, root-cause approach to restore the gut-immune balance.
Step 1 – Reduce Inflammation & Remove Triggers
- Anti-inflammatory nutrition
- Gluten- and dairy-reduction
- Removal of irritants: sugar, processed foods
- Addressing infections (SIBO, Candida, parasites)
Step 2 – Restore the Gut Lining
- L-glutamine
- Zinc carnosine
- Omega-3s
- Collagen peptides
- Soothing herbs: Aloe vera, slippery elm, licorice
Step 3 – Rebuild the Microbiome
- Targeted probiotics
- Prebiotic fiber
- Fermented foods
- Lifestyle changes (sleep, stress reduction)
Step 4 – Rebalance Immunity
- Reducing autoimmune triggers
- Healing inflammatory pathways
- Supporting hormone balance
- Targeted supplementation for immune support
This whole-person model improves digestion, immune function, metabolism, energy, and long-term wellness.
Healing the Gut–Immune Connection: Lifestyle Strategies
1. Adopt an anti-inflammatory diet
Focus on:
- Vegetables
- Lean protein
- Healthy fats
- Bone broth
- Gluten-free whole foods
- Low-sugar meals
2. Manage stress
Chronic stress weakens the gut lining and disrupts immunity.
3. Prioritize sleep
7–8 hours helps restore gut lining repair processes.
4. Avoid gut irritants
Limit:
- Alcohol
- Sugar
- Processed foods
- Artificial sweeteners
- NSAIDs
5. Support your microbiome
Add:
- Probiotics
- Fiber
- Fermented vegetables
When to Seek Medical Help
If you experience:
- Ongoing IBS symptoms
- Bloating after every meal
- Chronic fatigue
- Skin flare-ups
- Joint pain
- Autoimmune symptoms
- Unexplained inflammation
— It’s time to get a gut-immune evaluation.
Early intervention prevents long-term damage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q. What exactly is leaky gut?
Ans : It’s a condition where the intestinal lining becomes damaged, allowing toxins and food particles to leak into the bloodstream and trigger inflammation.
Q. Can IBS cause leaky gut?
Ans : Yes, IBS is associated with inflammation and altered gut barrier function, which can contribute to intestinal permeability.
Q. Can a leaky gut cause autoimmune disease?
Ans : Leaky gut is considered one of the major root triggers of autoimmune conditions because it activates and confuses the immune system.
Q. Which autoimmune conditions are linked to gut health?
Ans : Hashimoto’s, Crohn’s, RA, celiac disease, psoriasis, lupus, MS, and type 1 diabetes.
Q. How do you test for leaky gut?
Ans : Stool tests, intestinal permeability tests, food sensitivity panels, and inflammatory markers.
Q. Can leaky gut be reversed?
Ans : Yes. With proper nutrition, lifestyle changes, and targeted supplements, the gut lining can heal.
Q. Are probiotics enough to fix leaky gut?
Ans : Probiotics help, but gut healing usually requires a combination of diet, inflammation control, and repairing the gut lining.
Q. Can stress cause leaky gut?
Ans : Yes. Chronic stress weakens the gut barrier and disrupts the microbiome.
Q. What foods should I avoid?
Ans : Processed foods, sugar, alcohol, gluten, excessive dairy, and artificial additives.
Q. How long does gut healing take?
Ans : Most patients see improvement in 4–12 weeks with consistent lifestyle and treatment.
Ready to Heal Your Gut and Rebalance Your Immune System?
If you’re experiencing IBS symptoms, chronic inflammation, or autoimmune issues, don’t ignore the signs.
Patients Medical offers integrative gut-immune evaluations, advanced testing, and personalized treatment plans to help you heal from the inside out.
👉 Book your consultation today
Take the first step toward restoring gut balance, energy, and long-term health.

Dr. Kulsoom Baloch
Dr. Kulsoom Baloch is a dedicated donor coordinator at Egg Donors, leveraging her extensive background in medicine and public health. She holds an MBBS from Ziauddin University, Pakistan, and an MPH from Hofstra University, New York. With three years of clinical experience at prominent hospitals in Karachi, Pakistan, Dr. Baloch has honed her skills in patient care and medical research.